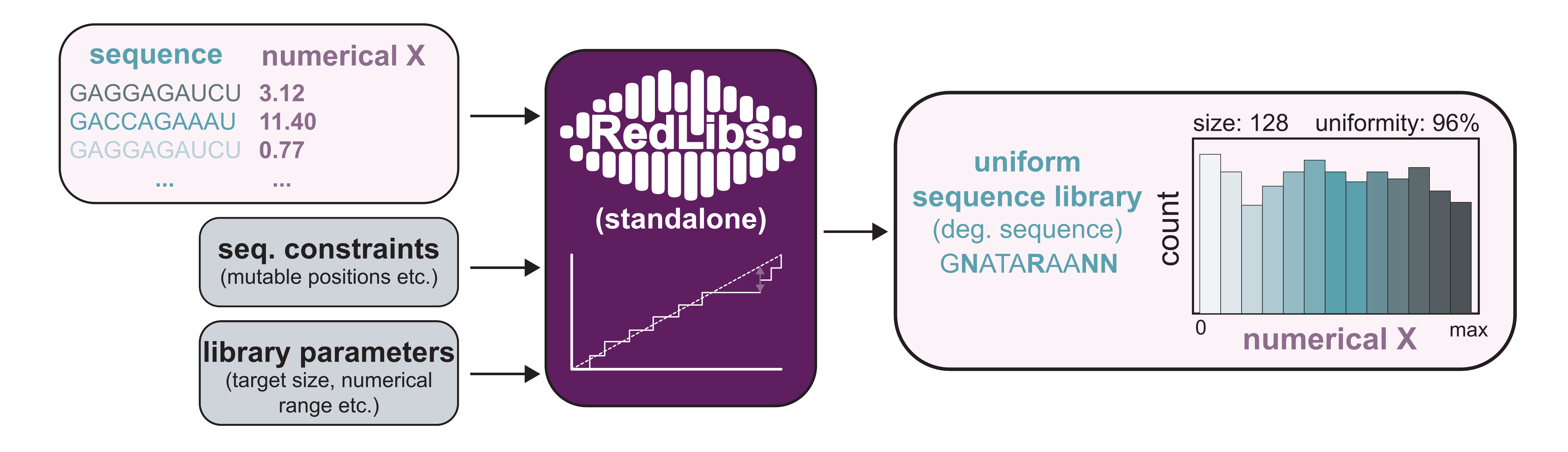
RedLibs (standalone) is a tool that generates sequence libraries that follow a uniform distribution
for a user-specified numerical sequence parameter while being encoded by individual
degenerate sequences
for facile cloning. These libraries have a user-defined size (i.e. number sequence variants encoded by
the degenerate sequence).
User manual
RedLibs (standalone) offers the same library design capabilities as the main RedLibs tool in rbsXpress.
However, the input data is not derived from the RBS Predictor allowing the user to add their own data sets
to generate uniform libraries from.
First input mask (data input)
First, the user can specify a list of comma-separated sequence-value pairs either via the query window or file upload (*.txt
files). Note that any type of DNA/RNA sequences (A, C, G or T/U) are accepted as long as they have the same length. The values
may correspond to any predicted or measured numerical feature associated with each sequence, whose distribution is to be
optimized by RedLibs(standalone).
Example:
AGAAAAAAATAATTGGA,0.05807638
AGAAAAACATAATTGGA,0.055958934
AGAAAAAGATAATTGGA,0.12676555
AGAAAAATATAATTGGA,0.05761717
AGAAAACAATAATTGGA,0.048265565
AGAAAACCATAATTGGA,0.049254492
...
Second input mask (library constraints)
Next, different target parameters for the designed libraries can be specified. The only required parameter here is the
Target library size, which corresponds to the number of individual sequences (i.e. library members) that the designed
library will contain. This parameter defines the resolution (i.e. the number of discrete levels), with which the range of the
numerical input parameter will be covered. It should be selected in agreement with the experimental throughput, at which
library members can be tested afterwards.
→
Result: RedLibs(standalone) will suggest libraries with a size of 32 sequences encoded by single, degenerate master
sequences, which follow a uniform distribution between the minimum and maximum value of the numerical in the input data
set.
Under Advanced options, additional library parameters can be defined (see mouseovers for detailed information).
Lower/Upper parameter threshold may be used to set lower and upper boundaries for the range of the numerical that
should be uniformly covered (default: min and max of input data set). No. of top solutions defines the number of
top libraries that RedLibs(standalone) suggests in the output (default: 10).
Output
The output of RedLibs(standalone) consists of two files detailing the results of library optimization in a text-based
(*.txt) and graphical (*.png) form.
The main output file (*.txt) is a comma-separated list of the optimized libraries in order of decreasing
uniformity.
It contains key information about the top libraries and their individual members. Each individual library member is represented
by one line with four columns specifying its sequence (“# sequence”) and value of the numerical (“numerical”) as well
as the degenerate sequence (“library”) and size (“size”) of the library it belongs to. A fifth column provides the
uniformity
(“uniformity_(%)”) as a score indicative of library quality with 100% corresponding to a perfectly uniform library matching
the target distribution.
The graphical output (*.png) additionally visualizes key features of the top libraries. It entails a histogram representation of
the numerical's distribution including a header containing the degenerate sequence, size and uniformity score for each library.
Example (*.txt):
| # sequence,numerical,library,size,uniformity_(%) |
|
| AGATGGGTTGTATTGGA,0.107,AGATGGRKKGNATTGGA,32,93.9 |
[1] |
| AGATGGATTGTATTGGA,0.257,AGATGGRKKGNATTGGA,32,93.9 |
[2] |
| AGATGGGGTGTATTGGA,0.533,AGATGGRKKGNATTGGA,32,93.9 |
[3] |
| ... |
|
| AGATGGAGGGAATTGGA,0.794,AGATGGRKKGNATTGGA,32,93.9 |
[32] |
| AGATGGGTTGTATTGGA,0.107,AGATGGRKKRYATTGGA,32,93.7 |
[33] |
| AGATGGATTGTATTGGA,0.257,AGATGGRKKRYATTGGA,32,93.7 |
[34] |
| AGATGGGGTGTATTGGA,0.533,AGATGGRKKRYATTGGA,32,93.7 |
[35] |
| ... |
|
| AGATGGAGGACATTGGA,0.706,AGATGGRKKRYATTGGA,32,93.7 |
[64] |
| ... |
|
→
In this example, a target library size of 32 was applied. Thus, the first 32 entries are members of the Top1 library, which share
the same degenerate sequence and uniformity score. Top2 library: entries 33-64, Top3 library: entries 65-96, etc..
Example (*.png):
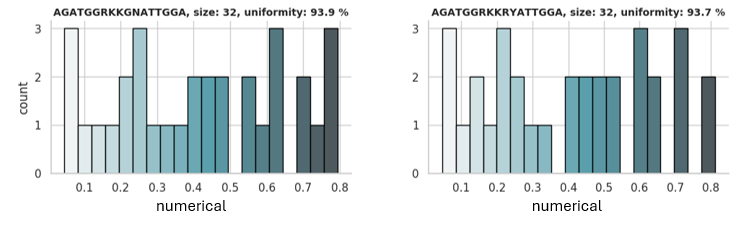
→
In this example, the graphical representation of two top libraries with a size of 32 is shown. The libraries are encoded by sequences
AGATGGRKKGNATTGGA and AGATGGRKKRYATTGGA, respectively, and cover the numerical's range between 0 and 0.8 with good
uniformity.
When you use the RedLibs in your published work, please do not forget to cite:
- Jeschek, M., Gerngross, D., & Panke, S. (2016).
Rationally reduced libraries for combinatorial pathway optimization minimizing experimental effort.
Nature communications, 7, 11163
(https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11163)